reason
- Low physical activity and sedentary lifestyle;
- Mechanical injury to the neck;
- When working sedentary for long periods of time, the cervical spine is subjected to high static loads;
- Uncomfortable mattresses and pillows;
- obesity;
- circulatory system diseases;
- scoliosis and other postural defects;
- Connective tissue dysplasia;
- Metabolic disorders.
Syndrome and symptoms

- Tinnitus - usually occurs when changing positions after remaining in a stationary position for a long time;
- Dizziness - the patient periodically feels as if an object begins to spin before his eyes;
- Pain in the neck and back of the head - the intensity of the pain depends on the degree of pathological changes;
- Feeling of lack of air - the patient is unable to take deep breaths;
- Visual impairment - occurs in later stages;
- Nausea, vomiting - also associated with impaired blood supply to certain parts of the brain due to deformed discs compressing key arteries;
- Sore throat, dry throat, foreign body sensation;
- changes in pressure that are poorly controlled with medications;
- numbness in fingers;
- Shoulder pain.
- pain when turning the neck;
- Can not move;
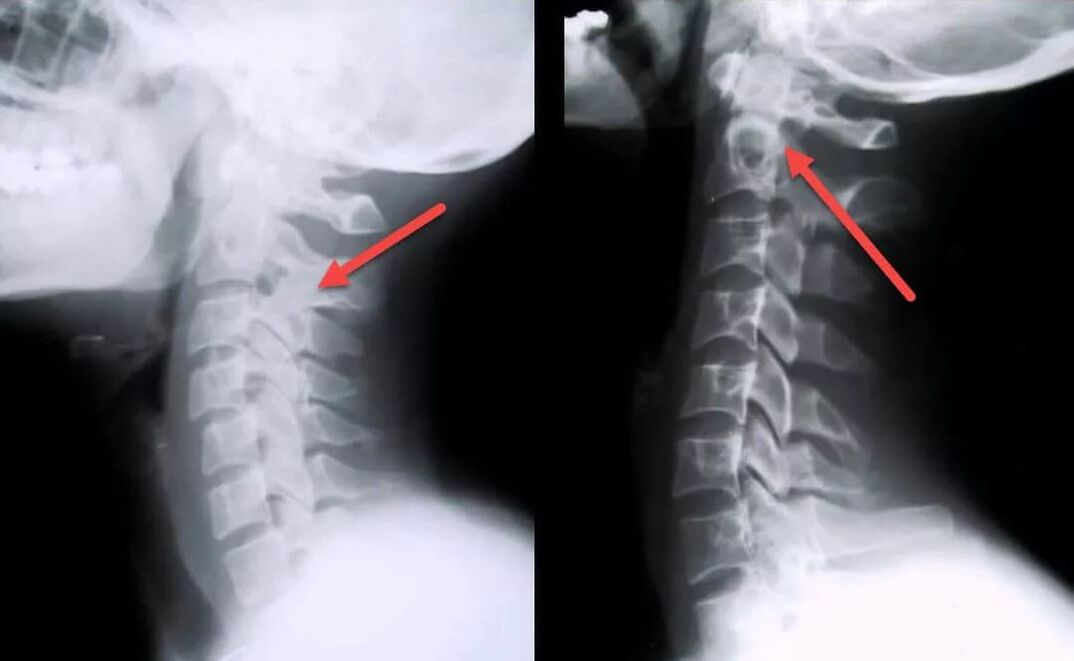
- X-rays showed signs of damage to the vertebrae and discs.
- burning and pain in the chest;
- Increased fatigue and unexplained weakness;
- Tachycardia.
stage
- The patient experiences mild discomfort in the neck. The disc begins to lose stability.
- Pain occurs. The disc deforms, the annulus fibrosus begins to break down, and the vertebrae move closer to each other.
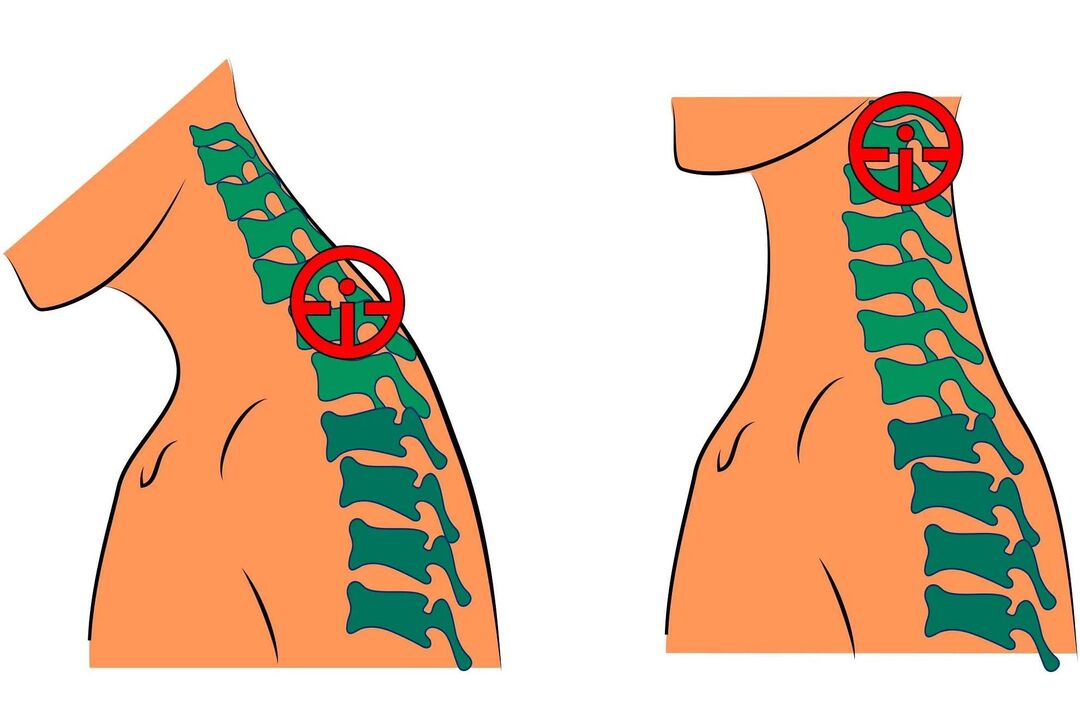
- Neck movement is restricted. Nausea and dizziness may occur when you turn your head. A persistent lack of blood to the brain can lead to symptoms such as lethargy, weakness, decreased performance, and fatigue. The intervertebral discs become thinner, the vertebrae begin to rub against each other, and the annulus fibrosus is destroyed, forming an intervertebral hernia.
- The neck cannot move and the blood supply to the brain is completely cut off. To correct this condition, patients must constantly take special medications. The vertebrae begin to fuse together.
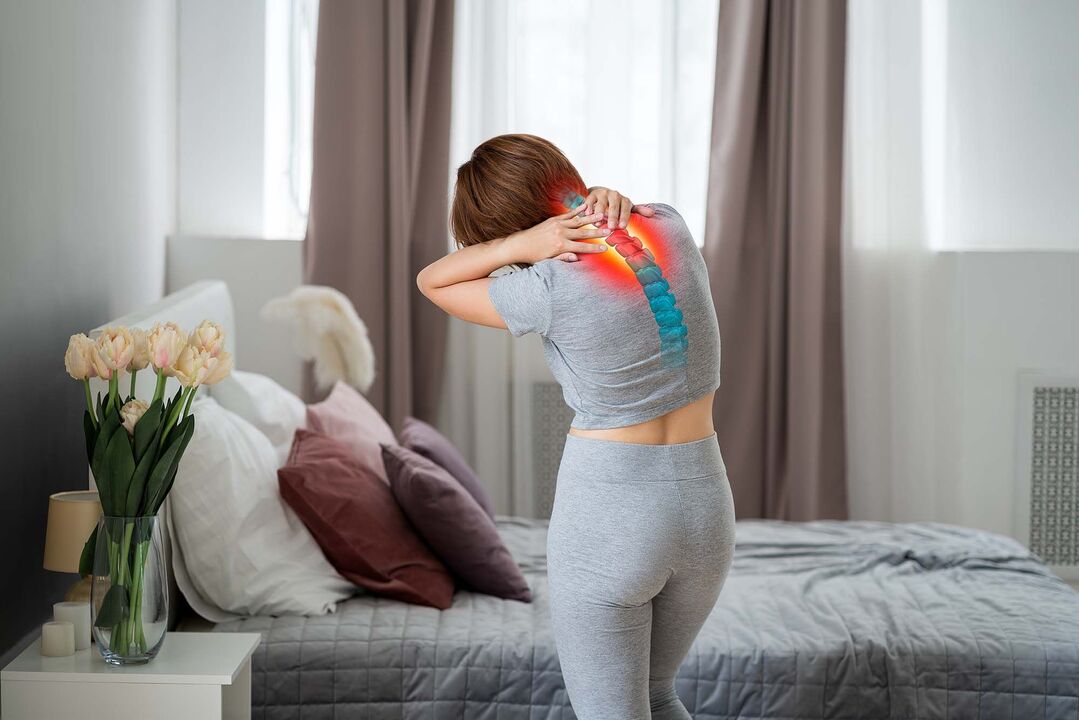
diagnosis
- blood analysis;
- Neck MRI - you can identify pathological changes even in the initial stages of the disease, when clinical manifestations are not yet obvious; with this study you can evaluate the current condition of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, identify the presence of deformations, osteophytes, compression of nerves and blood vessels;
- Carotid artery Doppler - can assess the degree of pressure and damage to blood vessels as well as the speed of blood flow;
- Myelography using contrast material - allows you to identify pinched nerves;
- Electrocardiogram - used for differential diagnosis with cardiovascular disease.
treat
- NSAIDs. Effectively relieves inflammation, pain, and swelling. These are symptomatic treatments that do not affect the cause of the disease. NSAIDs can be used in short courses of 10-14 days.
- Vasoprotectant, meant to speed up blood flow. Improve cerebral circulation and protect blood vessels from damage.
- Glucocorticoids. Effectively relieves pain and nerve compression. These medications have many side effects and should only be taken as prescribed by your doctor if NSAIDs and analgesics do not help.
- Chondroprotectant. Improves disc health and affects the cause of disease. They inhibit the destruction of cartilage tissue and improve the shock-absorbing properties of the intervertebral disc.
- Exercise therapy. Regular training can strengthen muscles and relieve cramps. It is recommended to conduct courses under expert guidance (at least in the initial stage)
- Manual therapy. Neck muscle spasm is one of the main causes of pain in this disease. Manual therapy, done correctly, can help eliminate spasms, blood vessels, and nerve compression. As a result, the nutrition of the intervertebral discs improves, cerebral circulation normalizes, and pain disappears.
- Intramuscular Theo Taping. Special tape is used to relax muscles and relieve spasms, swelling, inflammation while keeping the spine in the correct physiological position.
- Orthopedic equipment. In order to minimize the burden on the cervical spine, it is recommended to use orthopedic mattresses and pillows for sleeping. In addition, some patients are recommended to wear a special device (Schanz collar) to hold the neck in the correct position.
- massage. Effective treatments for cervical disease. Perfectly relieves swelling, pain, and congestion, improves local blood circulation, and relieves muscle spasms. Do not massage if you have acute neck pain.
- physiotherapy. Another effective technique. Conferences are held in the form of courses and are held several times a year. This allows you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, relieves muscle spasms, and slows further progression of the disease. For the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, mechanical therapy, traction therapy, hydromassage, UVT and mud therapy are most commonly used.
- Surgery to remove an intervertebral hernia;
- Removal of the vertebral arch or spinous process can relieve pressure on the roots of the spinal cord;
- Part of the disc core is removed to repair the herniation.
complication
- ventricular septal defect;
- lack of oxygen to the brain;
- arterial hypertension;
- Blurred vision, retinal dystrophy;
- respiratory spasms;
- Swallowing behavior is violated due to esophageal dysfunction;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Neck muscle spasm and numbness;
- Chronic pain in the upper body that cannot be relieved by analgesics;
- Hormone imbalance.
prevention
- maintain posture;
- Properly equip the workplace to avoid neck strain;
- Healthy Food;
- Stop smoking and drinking;
- Avoid neck injuries;
- Exercise more and exercise;
- Do not overcool;
- Weight control;
- sleep on special orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- Do regular gymnastics to avoid congestion;
- Prevent spinal curvature;
- Get regular massage sessions to improve blood flow and relieve congestion;
- Do not keep your head tilted forward for long periods of time;
- If you experience neck discomfort, you need to make an appointment with a specialist for examination. This will help detect possible changes in the intervertebral disc early, thus greatly facilitating treatment and improving prognosis.